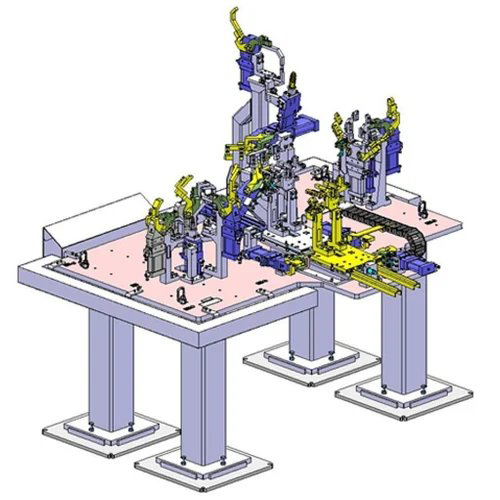
Welding Fixture
Welding Fixture Specification
- Usage
- Industrial
- Size
- Standard
- Color
- Silver
Welding Fixture Trade Information
- Minimum Order Quantity
- 1 Unit
- Payment Terms
- Cash in Advance (CID)
- Supply Ability
- 50 Units Per Month
- Delivery Time
- 2-10 Days
- Main Export Market(s)
- Asia
- Main Domestic Market
- All India
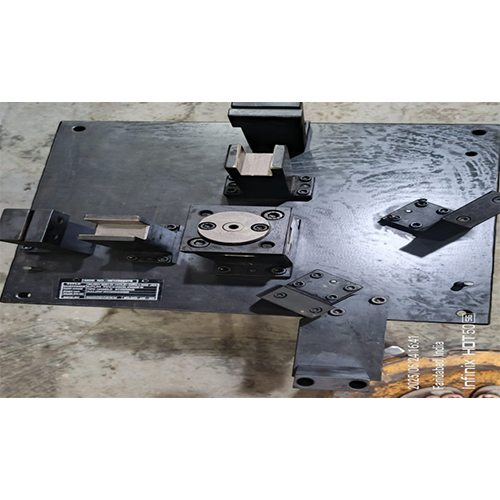
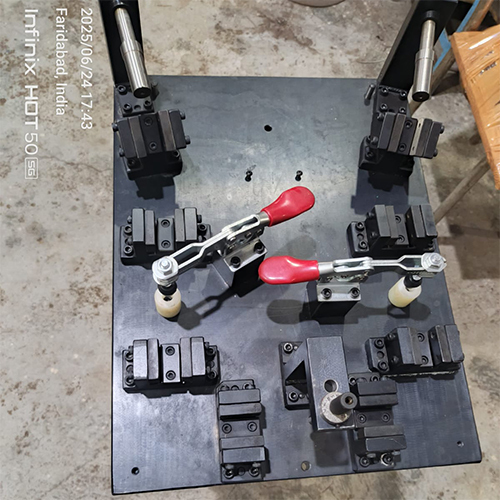
About Welding Fixture
welding fixture is a specialized tool designed to accurately position and securely hold workpieces during the welding process. It ensures precise alignment, minimizes distortion, and enhances the overall quality and efficiency of welding operations. Essentially, it's a jig that helps welders achieve consistent and reliable results.
Key functions and benefits of welding fixtures:
-
Welding fixtures precisely locate and hold components, ensuring they are in the correct alignment for welding.
-
By firmly supporting the workpiece, fixtures minimize the potential for distortion or warping caused by the heat of welding.
A welding fixture is a specialized tool or device used to hold and locate workpieces accurately and securely during the welding process, ensuring precise alignment and minimizing distortion. These fixtures are crucial for achieving consistent, high-quality welds, especially in mass production, by providing stable support and preventing movement. Key components include locators and clamps, with fixtures made from strong materials like steel to withstand welding heat and stresses.Purpose and Benefits- Accuracy & Precision: Guarantees that components are positioned correctly for welds that meet specifications.
- Repeatability: Enables consistent results, which is vital for mass production.
- Distortion Elimination: Helps to prevent warping and misalignment of materials due to heat and welding stresses.
- Productivity: Reduces lead time and simplifies the job setting process for the welder, increasing output.
- Safety: Securely holds components, reducing operator risk during welding.
- Quality: Leads to a better, more uniform quality of the final welded part.
Components of a Welding FixtureA typical welding fixture is built with several essential components:- Fixture Body/Base: The main structural component of the fixture.
- Locators: Parts that precisely position the workpiece in the desired orientation.
- Clamps: Devices used to firmly hold the workpiece against the locators and supports.
- Supports: Structures that provide stability to the workpiece.
ApplicationsWelding fixtures are used across various industries and applications:- Automotive: For welding vehicle frames and components.
- Structural Welding: For precise alignment of large structural parts.
- Manufacturing: In processes requiring high precision and repeatability.
- Robotic Welding: To facilitate automated welding operations.
- Accuracy & Precision: Guarantees that components are positioned correctly for welds that meet specifications.
Tell us about your requirement

Price:
Quantity
Select Unit
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
Additional detail
Mobile number
Email
More Products in Welding Fixture Category
Bush Welding Fixture
Price 75000 INR / Unit
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Unit
Color : Black
Product Type : Bush Welding Fixture
Application : Industrial
Material : Iron
Carrier Support Welding Fixture
Price 60500 INR / Unit
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Unit
Color : Grey
Product Type : Carrier Support Welding Fixture
Application : Industrial
Material : Iron